Gastric sleeve Turkey is a surgical operation that reduces the size of the stomach to approximately 15% of its original size. The stomach is removed along the greater curvature and a tube-like structure is inserted inside.
How Does Gastric Sleeve Work? A patient’s appetite is controlled by a hormone called Ghrelin, which decreases after a gastric sleeve Turkey operation.
This reduces the amount of food a patient eats during a single meal. As a result, the body is able to adjust to a healthier set point.
Because the surgery limits the volume of the stomach, food passes through the digestive system in the normal order, allowing vitamins and nutrients to be absorbed. Patients are usually able to resume their normal activity level after the surgery.
During the procedure, a specialized tool called a trocar is used to access the stomach outlet. After this, the surgeon inserts a silicone tube into the stomach outlet. This silicone tube separates the stomach’s adipokines tissue. The excess stomach tissue is then cut with staples. The resulting sleeve reduces the volume of the stomach to 80-150 ml.
While gastric sleeve surgery Turkey can lead to weight loss, complications can arise afterward. Patients are required to make a lifelong commitment to healthier eating habits after the surgery. Changing eating habits and exercising are key to a successful outcome. Patients should prepare for this lifestyle change for at least four to five years before surgery. They should also consult a nutritionist if they have any questions.
The sleeve gastrectomy is the most popular type of bariatric surgery. This surgery limits the amount of food a patient can eat and regulates metabolism. It also helps establish a lower set point of body fat for the patient. The procedure is considered the gold standard in the weight loss surgery field by many experts. Because of its success rate, the procedure is now the preferred method of weight loss surgery for many people.
years of experience

Since a gastric surgery is an invasive procedure that can also result in many complications, there are some requirements that must be met for the operation.
In the case of a gastric surgery Turkey, there should be no addictive disorders (such as drugs, tablets or alcohol), as this could lead to a shift in addiction. Because food addiction is no longer possible due to the smaller stomach, some patients switch to other addictive substances. People suffering from depression cannot have surgery either.
The patient must be motivated to complete the treatment, as an operation to reduce the size of the stomach alone is not enough. After that there are strong restrictions in everyday life, in particular the regulations for the following diet. The patient must be informed about all risks.


The desired weight reduction can be achieved through various methods. Some involve reducing the size of the stomach itself (restrictive techniques) and others bypassing the stomach in the digestive tract (bypass techniques).
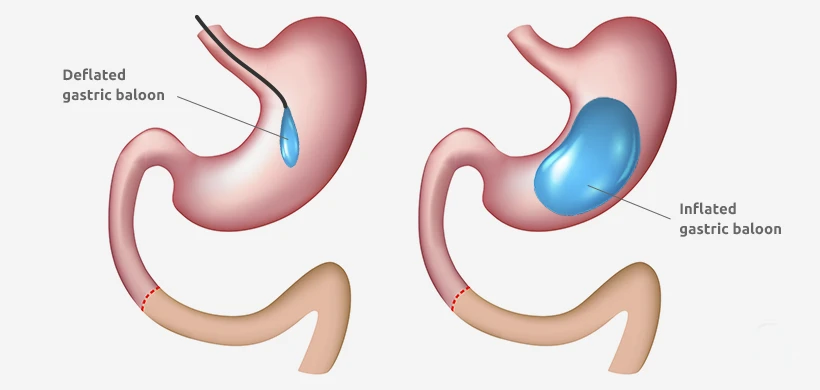
With the restrictive methods, the stomach is reduced in size using a so-called gastric band or similar methods. That’s why you feel full even after eating very small amounts of food and you automatically eat less. Digestion is less affected with these methods because all parts of the stomach are still present. However, it can still happen that you don’t maintain your reduced weight so easily if you don’t eat disciplined. Liquid or mushy food can easily pass through the reduced stomach and is fully digested, i.e. all calories are absorbed. This would be especially dangerous with ice cream, pudding, and sodas of all kinds.

With the bypass methods, the stomach is bypassed directly, i.e. the esophagus is separated from the stomach and sewn directly back onto the duodenum. With this method, the food is digested to a lesser extent and thus fewer calories are absorbed, so the various bypasses belong to the malabsorptive (little or bad food intake) methods.
Despite the benefits of gastric sleeve Turkey, there are some disadvantages associated with the procedure. For one, patients must make certain lifestyle changes after the surgery. It will require a change in eating habits. A person must also commit to a certain exercise program. Depending on their needs, gastric sleeve surgery may also require some additional lifestyle changes, such as taking calcium supplements or attending preoperative lifestyle classes.
The gastric sleeve procedure is generally only for people with a BMI of 40 or above. Those who are more than 100 pounds over their ideal weight may be a good candidate.
The gastric sleeve surgery, can drastically reduce appetite and help patients lose weight permanently.
Moreover, it can help them maintain a healthy lifestyle for the long-term. The gastric sleeve surgery can help individuals lose 50 to 60 percent of their excess body weight. Because of this, it has the potential to improve many areas of health.
Although a gastric sleeve surgery in Turkey may have little pain, the results are often amazing.
In addition to weight loss, patients can also experience reduced gallbladder and urinary stones.
This is because stomach acid contributes to the development of urinary stones. Additionally, gastric surgery can reduce the risk of gallbladder disease and gastric cancer. Because the stomach is only partially removed in the surgery, the risks of these two complications are minimized.



Since these are very overweight patients, who often also suffer from comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus and high blood pressure, surgical interventions are generally more risky than in healthy patients and require special attention. Even after the operation, complications such as wound healing disorders are more common in such patients. In addition, overweight patients have an increased risk of thrombosis or embolism.
Patient Satisfaction
Each patient receives one-on-one attention with a smiling face.
High-end Technology
Patients are treated with an extremely high level of surgical expertise.
Budget Friendly
We are thinking of you with affordable prices and the opportunity to pay in installments.

After gastric sleeve surgery, patients can eat normal, healthy food again. The recovery time is three to four weeks, and the patient will need to have regular checkups with their doctor. They will also need to make a commitment to eating right and exercising for the rest of their lives.
While this surgery can result in drastic weight loss, it is not without side effects. Some patients report a low tolerance for hot and spicy foods.
During the first few weeks after surgery, patients usually recover well. Most are back to work within two weeks, but vigorous exercise should be delayed until at least four weeks. The patient can still take prescribed medications, although they may need to be broken into smaller pieces. Common diabetes and blood pressure tablets are fine to take. In addition, it may be necessary to have someone stay home with the patient while they are healing.
Although gastric sleeve surgery is a safe procedure, complications and mental health problems are possible after surgery. Some patients experience difficulty absorbing nutrients after the procedure and suffer from heartburn and reflux.
If the problem is severe enough, you may consider gastric bypass surgery. There are many options for stopping reflux and heartburn after surgery. You should talk to your healthcare team to determine which option is best for you.
What happens during gastrict sleeve surgery? Anesthesia is given before surgery. The patient remains under the influence of anesthesia throughout the operation.
vaser liposuction breaks down fat cells and allows them to be loosened from deep tissues. As a result, stubborn fat deposits are removed from the application area much more easily and effectively. This is achieved by the powerful waves of Vaser technology, which breaks the bonds between fat cells. However, like all other liposuction methods, Vaser liposuction should be applied by plastic surgeons with sufficient experience and expertise.

There are several differences between the procedures Gastric Bypass and Gastric Sleeve. Both surgeries reduce stomach size. The Gastric Bypass surgery bypasses the small intestine, which leads to reduced food absorption and a smaller stomach pouch.
Recovery time varies between the two procedures. While both procedures require recovery time, a gastric sleeve recovery period is typically shorter, taking four to six weeks.
The recovery time after a gastric bypass surgery varies from patient to patient but in general, the sleeve surgery procedure will leave the patient on a liquid diet for a few weeks. This will progress to solid foods over the following weeks. Initially, patients will have to consume smaller portions of food than they normally do and will not be able to drink or smoke during meals.
The results of gastric surgery depend on many factors, including the patient’s general health and medical history. The long-term success of gastric surgery will depend on the patient’s lifestyle and weight goals.
Although both procedures have similar success rates, gastric sleeve surgery is more effective in treating obesity than the Gastric Bypass procedure. In addition, patients can achieve the same health improvements as a Gastric Bypass patient, with fewer complications.
If you want to have sleeve gastrectomy surgery in Turkey, we should definitely be your priority.
We provide a more professional service with our specialist doctors and latest generation devices.